
![]()
![]()

Updated on 05/05/2015
BusAd 175: Introduction to International Trade
Spring 2011
Course #3819
Apr 18 - Jun 8, 2011
Home My Book My Physical Geology Pages My Oceanography-115 class My Environmental Geology Pages
|
|
|
|
Updated on 05/05/2015 |
|
|
BusAd 175: Introduction to International Trade |
Spring 2011 Course #3819 Apr 18 - Jun 8, 2011 |
|||
|
Home My Book My Physical Geology Pages My Oceanography-115 class My Environmental Geology Pages |
||||
|
My BusAd classes: BusAd-101 (General Business), BusAd-170 (International Business), BusAd-175 (International Trade) BusAd-178 (International Finance) |
|
Chapter Outlines, Sample Tests and Review Questions |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 14:
|
Government Export Financing Programs | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Information and materials on this page are based on those provided by the author, Dr. Belay Seyoum Chapter Outline Background
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Export-Import Bank of the United States (Eximbank)
|
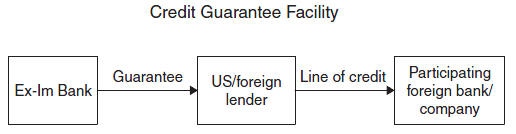 |
Major Export Financing Programs Provided by Eximbank
|
|
Working Capital Guarantee Program
|
|
|
Export Credit Insurance Program
|
|
|
Small Business Administration (SBA) |
|
 |
Guarantees loans to small businesses that are already engaged or plan to engage in international trade as well as those which are adversely affected by import competition.
The SBA can guarantee as much as $1,250,000 in combined working capital (provided under the EWCP), and facilities and equipment loans.
- SBA Export Express
SBA Export Express is a flexible financing tool available to assist small businesses in developing and expanding export markets.
Approved lenders use streamlined and expedited loan review and approval procedures.
SBA provides participating lenders with a payment guarantee up to a maximum loan amount of $250,000.
|
|
Overseas Private
Investment Corporation (OPIC)
|
|
|
|
|
Private Export
Funding Corporation (PEFCO)
|
|
|
Department of
Agriculture:
The USDA provides financial support for export of U.S. agricultural
products through GSM–102, GSM–103, and Public Law 480. |
|
|
State and Local
Export Financing Programs:
States provide different programs to expand exports: loans, loan
guarantees. They also act as delivery agents for Eximbank programs. |
|
|
|
True |
False |
||
| 1. |
Exporters prefer to be paid
on or before shipment of the goods, whereas buyers want to delay payment
until they have sold the merchandise. |
||
| 2. |
Forms of
external financing includes debt or equity financing,
short-term/intermediate/long-term financing, and investment, inventory, or
working capital financing. |
||
|
Which
of the following explains why Ex-Im Bank’s role in promoting U.S. exports is
likely to be more significant now than in the past few decades? |
|||
|
3. |
|
|
The U.S. economy is more internationalized, and imports constitute a growing share of the GNP |
|
4. |
|
|
The volume of international trade has substantially increased, and competition for export markets is quite intense. |
|
5. |
|
|
The U.S. economy is more internationalized, and exports and imports constitute a growing share of the GNP |
|
True |
False |
|||||
|
The
practice of purchasing deferred debts arising from international sales contracts without recourse to the exporter is called ... |
6. |
Forfaiting |
|
|
|
|
|
7. |
Discounting |
|
|
|
||
|
8. |
Discrepancy |
|
|
|
||
| Which of these is an example of internal, as compared to external, financing? |
9. |
Family and friends | ||||
|
10. |
Attracting venture capital. | |||||
|
|
What is the difference between buyer and supplier credit?
Supplier credits are extended to the buyer by the exporter, that is, the exporter arranges for financing or directly extends credit to overseas buyer. Buyer credits are extended to overseas customers by parties other than the exporter, such as government agencies and banks and other private agencies.
State the OECD guidelines on export credits.
A minimum of 15% of the contract price to be paid in cash, maximum repayment term of eight and a half years (except for poor countries), minimum interest rates for set periods, gradual abolition of subsidized interest rates.
Describe the origins and activities of the Ex-Im Bank.
Ex-Im Bank was created in 1934 and established under its present law in 1945 to assist in the financing of U.S. export trade. Ex-Im Bank provides guarantees and export credit insurance as well as competitive financing to foreign buyers.
What are some of the criticisms of the Ex-Im Bank?
Criticism of the Ex-Im Bank: it provides financing for projects that harm the environment, domestic industries. Financing is provided to a small number of large U.S. firms such as Boeing, Bechtel, and General Electric.
What is the difference between the working capital guarantee program and the direct loans program?
Working Capital Guarantee Program: Ex-Im Bank will guarantee 90 percent of the loan provided to a U.S. exporter by a qualified lender. Under the direct loan program, medium/long-term loan is provided by Ex-Im Bank to creditworthy foreign buyers for the purchase of U.S. capital goods and services.
What kinds of exports are eligible under the working capital program?
To cover purchase of raw materials, finished goods for export, to pay for overhead and cover standby letters of credit.
Compare and contrast the single-buyer and multiple-buyer policy.
Single-buyer policy: covers a single sale or repetitive sale over a one-year period to a single buyer. A multibuyer policy covers short-term export sales to many different buyers. They are similar in terms of eligible exports, eligible exporters, and risks covered.
Discuss the role of OPIC in promoting U.S. exports.
OPIC insures U.S. investors against political and commercial risks. It provides financing through loans and loan guarantees.
How does PEFCO promote U.S. exports?
PEFCO works in conjunction with Ex-Im Bank in the financing of foreign purchases of U.S. goods and services. Its loans are guaranteed by Ex-Im Bank.
State some of the programs available to promote U.S. agricultural exports.
GSM-102, GSM-103, Public Law 480.