
![]()
![]()

Updated on 05/05/2015
BusAd 175: Introduction to International Trade
Spring 2011
Course #3819
Apr 18 - Jun 8, 2011
Home My Book My Physical Geology Pages My Oceanography-115 class My Environmental Geology Pages
|
|
|
|
Updated on 05/05/2015 |
|
|
BusAd 175: Introduction to International Trade |
Spring 2011 Course #3819 Apr 18 - Jun 8, 2011 |
|||
|
Home My Book My Physical Geology Pages My Oceanography-115 class My Environmental Geology Pages |
||||
|
My BusAd classes: BusAd-101 (General Business), BusAd-170 (International Business), BusAd-175 (International Trade) BusAd-178 (International Finance) |
|
Chapter Outlines, Sample Tests and Review Questions |
|
|
|
|
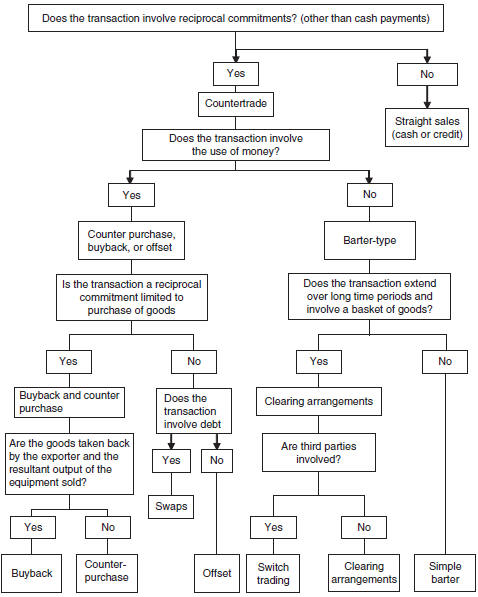
Chapter 12: Countertrade |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Information and materials on this page are based on those provided by the author, Dr. Belay Seyoum Chapter Outline What is Countertrade
Benefits of Countertrade |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||
|
|
|
Theories of Countertrade
Forms
of Countertrade
|
 |
||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||
 |
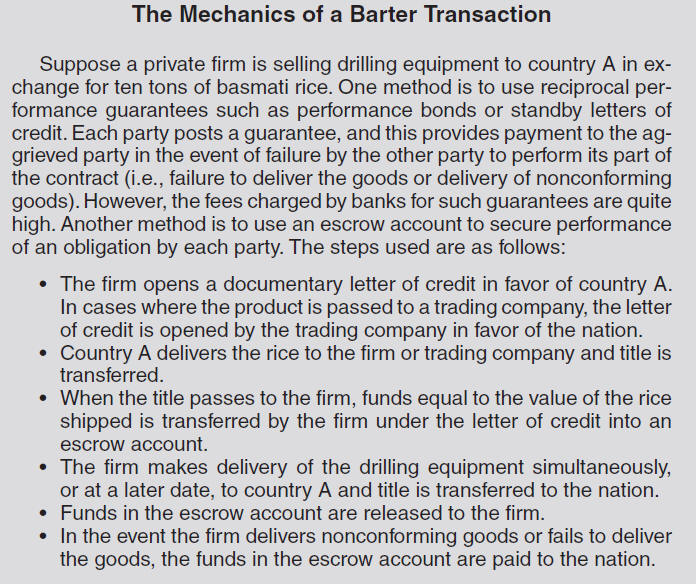
Offsets: A transaction in which an exporter allows the purchaser, usually a foreign government to reduce the cost of purchasing the exporter’s product by co-production ,sub-contracting, investments and transfers of technology.
Direct offsets:
Co-production: Joint venture or licensing arrangements with overseas customer.
Sub-contractor production: Arrangement for production in the importing country of parts or components of the export product destined to the latter.
Investments and transfer of technology : Certain offset agreements provide for investments and technology transfer to the importing country.
Indirect offsets: Offset arrangements in which goods and services unrelated to the exports are acquired from or produced in the importing country.
| Countertrade with the GATT/WTO |
|
||||||
| Concerns of the GATT/WTO with Countertrade |
|
||||||
| Countertrade and the International Monetary Fund |
|
||||||
| Government’s Attitude with Countertrade |
|
|
|
|
|
True |
False |
||
|
Which of these would you consider to be an example of countertrade? |
1. |
Lockheed Martin agreed to sell F-16 military aircraft to Hungary in exchange for large investment and counterpurchase commitments. The firm agreed to buy $250 million (U.S.) worth of Hungarian goods. |
||
| 2. |
Taiwan purchased 60 Mirage 2000-5 from a French aviation company, Dussault. In return, Dussault undertook a joint venture with Taiwan’s aerospace company, Chenfeng, for the production of key aircraft parts and components for local aircraft and export. |
|||
|
3. |
|
|
Indonesia negotiated
for a power station project with Asea Brown Boveri and for an
air traffic control system with Hughes Aircraft. |
|
|
The U.S. government prohibits ... |
4. |
|
|
the use of countertrade in international business transactions. |
|
5. |
|
|
federal agencies from promoting countertrade in their business or official contracts.
|
|
True |
False |
||
| 6. |
One of the benefits of countertrade for exporters is
transfer of technology. |
||
| 7. |
C ountertrade is quite common in countries where exchange control restrictions are in place. |
|
True |
False |
|||
|
In 1989, PepsiCo and the former Soviet Union signed a $3 billion deal in which PepsiCo agreed to purchase and market Russian Vodka and ten Soviet-built ocean vessels in return for doubling its Soviet bottling network and nationwide distribution of soft drinks in aluminum and plastic bottles. Is this an example of ... |
8. | countertrade? | ||
| 9. | barter? | |||
| 10 | counterpurchase? |
|
|
What are the major factors accounting for the resurgence of countertrade?
East-West trade, shortage of hard currency in many developing/East European countries.
What is the benefit of countertrade for exporters?
Increased sales opportunities, access to sources of supply, flexibility in prices.
“Countertrade is used as a substitute for FDI.” Discuss.
Multinational firms resort to countertrade when host countries impose restrictions on inward FDI.
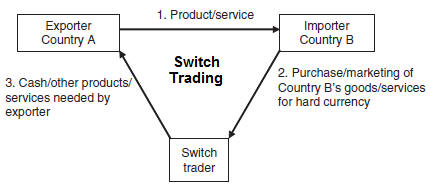
What is the difference between switch trading and clearing arrangement?
In switch trading, the switch trader will buy or market countertraded goods for hard currency. In clearing arrangements, two governments agree to purchase a certain volume of each other’s goods/services over a given period of time.
|
 |
|
 |