
![]()
![]()

Updated on 05/05/2015
BusAd 175: Introduction to International Trade
Spring 2011
Course #3819
Apr 18 - Jun 8, 2011
Home My Book My Physical Geology Pages My Oceanography-115 class My Environmental Geology Pages
|
|
|
|
Updated on 05/05/2015 |
|
|
BusAd 175: Introduction to International Trade |
Spring 2011 Course #3819 Apr 18 - Jun 8, 2011 |
|||
|
Home My Book My Physical Geology Pages My Oceanography-115 class My Environmental Geology Pages |
||||
|
My BusAd classes: BusAd-101 (General Business), BusAd-170 (International Business), BusAd-175 (International Trade) BusAd-178 (International Finance) |
|
Chapter Outlines, Sample Tests and Review Questions |
|
|
|
|
Chapter 13: Capital Requirements and Private Sources of Financing |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Information and materials on this page are based on those provided by the author, Dr. Belay Seyoum Chapter Outline Background
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Determinants of Capital Needs and Financing Alternatives
|
|
The principal determinants are (a) stage of evolution, (b) ownership structure and (c) distribution channels. |
|
|
A very small sum of money is often needed to start the business as an agent because no payments are made for merchandise, transportation, or distribution of the product. |
|
|
However, initial capital needs are substantial if a person starts the business as a merchant, distributor, or trading company with products available for resale. This entails payments for transportation, distribution, advertising and promotion, travel, and other expenses. |
|
|
Capital needs at the start–up
stage may be smaller compared to those needed during the growth and
expansion period. |
| Internal Financing |
|
Types External Financing
|
|
Debt or equity financing: Debt financing occurs when an export–import firm borrows money from a lender with a promise to repay (principal and interest) at some predetermined future date. |
|
|
Short–term, intermediate, or long–term financing: Short–term financing involves a credit period of less than one year, while intermediate financing is credit extended for a period of one to five years. |
|
|
Investment, inventory, or working capital financing: Investment financing is money used to start the business (computer, fax machine, telephone, etc). |
|
|
 |
||||||||||
|
|||||||||||
|
|
Private Sources of Export Financing |
|
|
|
|
|
Short–Term Methods
Intermediate– and Long–Term Methods
|
|
|
|
True |
False |
||
| 1. |
Many small and medium-sized
businesses suffer from undercapitalization and/or poor management of
financial resources, often during the first few years of operation. |
||
| 2. |
Forms of external financing includes debt or equity financing, short-term/intermediate/long-term financing, and investment, inventory, or working capital financing. |
|
True |
False |
||||
|
What type of financing occurs when an export-import firm borrows money from a lender with a promise to repay (principal and interest) at some predetermined future date? |
3. |
Short-term |
|
||
| 4. |
Intermediate |
|
|||
| 5. |
Debt |
|
|||
|
The
practice of purchasing deferred debts arising from international sales contracts without recourse to the exporter is called ... |
6. |
Forfeiting |
|
|
|
|
7. |
Discounting |
|
|
|
|
|
8. |
Discrepancy |
|
|
|
| Which of these is an example of internal, as compared to external, financing? |
|
9. |
|
|
Family and friends |
|
10. |
Credit cards |
|
|
What are the major changes taking place in small and medium-sized business financing?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
 |
|
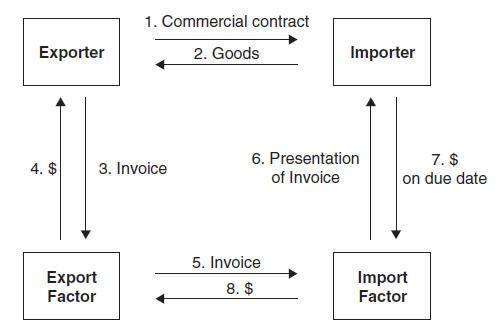 |
the export factor passes the invoice to the import factor for assumption of credit risk, administration, and collection of the receivables,
the import factor presents the invoice to the importer for payment on the agreed-upon date,
the importer pays the import factor, and
the import factor pays the export factor.
As explained in the table,
factoring is not available for low value shipments or for receivables
with a maturity of more than 180 days. Factors also do not work with
developing countries due to their inadequate legal and financial
framework. Exporter could be liable for disputes concerning
quality/condition of the goods.
No.
Minimum investment is between $50,000 to $100,000, they seldom provide
start-up capital, they expect high returns on their investments.
Microloans, export working capital, fast track, international trade loan, SBICs, CDC/504, 7(a) loan guarantee.