-
Supermarkets
and convenience stores comprise just two of the many elements that
make up distribution channels around the globe. The American
Marketing Association defines a channel of distribution as “an
organized network agencies and institution that, in combination,
perform all the activities required to link producers with users to
accomplish the marketing task”.
-
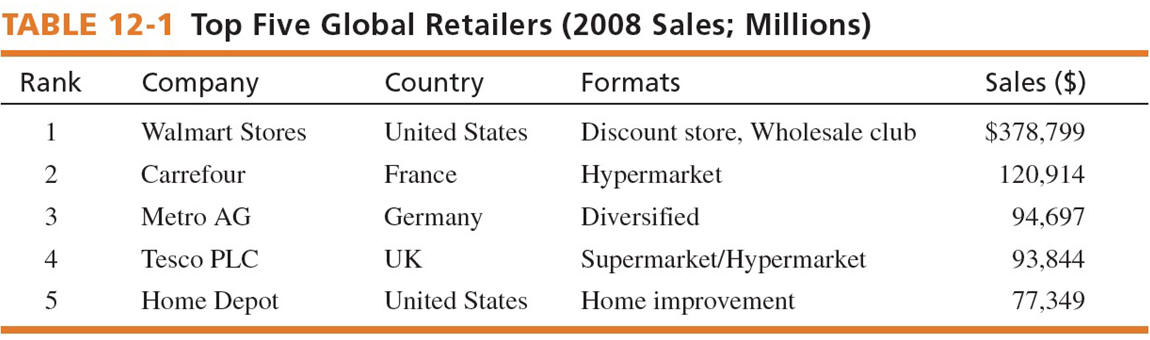
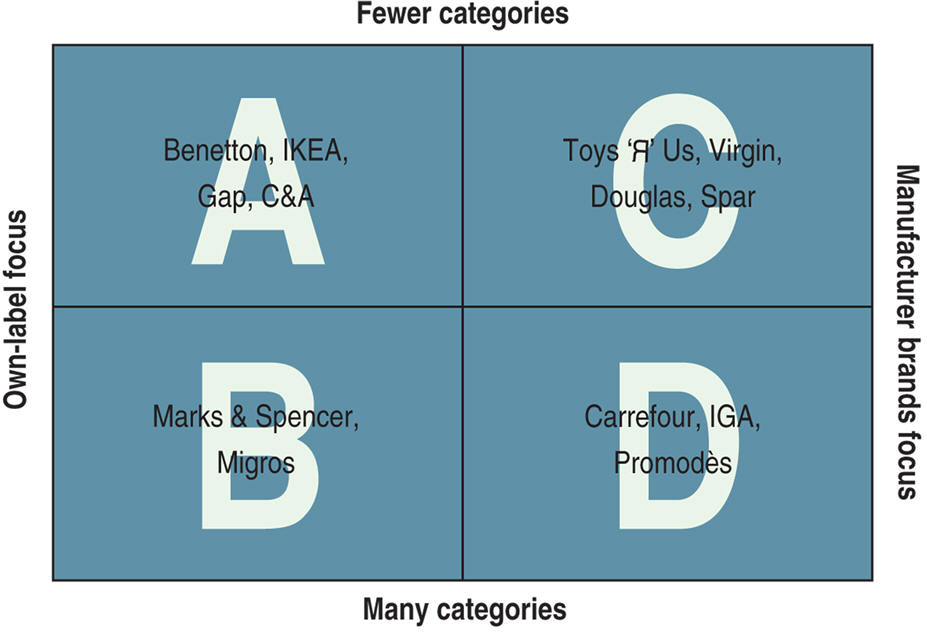
Distribution channels are one of the most highly differentiated
aspects of national marketing systems. Retail stores vary in
size from giant hypermarkets to small stores in Latin America
called pulperias.
-
The
diversity of channels and the wide range of possible
distribution strategies and market entry options present
challenges to managers responsible for designing global
marketing programs. Channels and physical distribution are
crucial aspects of the total marketing program; without them, a
great product at the right price and effective communication
means very little.
|
|
Chapter Overviews, Outlines, Sample
Questions
-
Introduction to Global Marketing
-
The Global Economic
Environment
-
Regional Market
Characteristics and Preferential Trade Agreements
-
Social and Cultural
Environments
-
The Political, Legal, and
Regulatory Environments
-
Global Information Systems
and Market Research
-
Segmentation, Targeting,
and Positioning
-
Importing, Exporting, and
Sourcing
-
Global Market Entry
Strategies: Licensing, Investment,
and Strategic Alliances
-
Brand and Product
Decisions In Global Marketing
-
Pricing Decisions
-
Global Marketing Channels
and Physical Distribution
-
Global Marketing
Communications Decisions I: Advertising
and Public Relations
-
Global Marketing
Communications Decisions II: Sales Promotion,
Personal Selling, Special Forms of Marketing
Communication
-
Digital Revolution
-
Strategic Elements of
Competitive Advantage
-
Leadership, Organization,
and Corporate Social Responsibility
|